WHAT IS THE BLOG ABOUT?
- IS CLOUD ARCHITECTURE THE GUIDING STRATEGY IN ANY CASE?
- WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING GOOD FOR?
- WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF CLOUD SOLUTIONS?
Cloud and hybrid solutions, license and access consolidation, cost optimization, data security
The evolution of IT infrastructure is a huge challenge for even the largest international companies. Keeping pace with the evolution of technology is not only a test of strength over time, but also a serious business policy consideration.
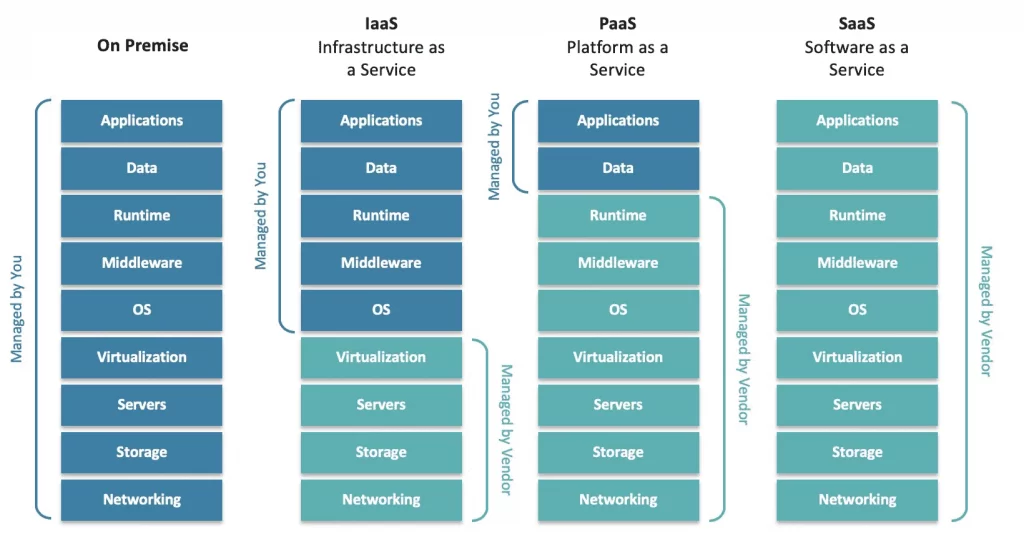
Cloud-based systems could be encountered more than two decades ago by anyone who had a mail account, so this is not today’s phenomenon. Cloud as a service is a very versatile option and is not just for data storage. Due to its full name, it is a computing medium that does not mean processing on a local device. As a result, it is extremely versatile and supports multiple levels of IT utilization such as IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service) or SaaS (Software as a Service). There is also a private cloud, but there are hybrid solutions as well, where, in addition to the on-premises servers, some cloud solution provides the foundation for the infrastructure.
IS CLOUD ARCHITECTURE THE GUIDING STRATEGY IN ANY CASE?
Due to the numerous possibilities of use, the development of the optimal infrastructure is of decisive importance for large companies, in addition to greater user access. This, in turn, can be called everything, but it is by no means an easy and self-evident task. Not least because everyone wants to know the data within the utmost security, and the physical indeterminacy of the cloud environment is the source of mistrust. Everyone has heard of cases where confidential customer data and access codes from a global service provider have fallen into unauthorized hands. From this, most can conclude that the cloud is a dangerous place. Of course, just like our phone or laptop what we can lose, and could be broken by unauthorized people or even destroyed in an accident. So the question is more about which one is easier to protect and which one is more useful to use for this or that. The most important thing to do is to get acquainted with the exact options, their advantages and disadvantages. This, in turn, would be a rather complicated acquaintance for most businesses, not coincidentally requiring the involvement of experienced professionals in infrastructure and application consolidation.
In addition to familiarizing yourself with the cloudy possibilities, there are, of course, pre-consolidation requirements, that for example determine the data management or geographical constraints of the business. And it is not a marginal issue to provide safe and at the same time flexible, fast service for business needs and work processes. Despite of cloud computing is the part of IT, it may not be necessary to store everything there or run it from there.
What solutions are available to meet your IT needs?
- On Premise, meaning a local service, where all resources, data storage, security organization are the responsibility of the local server. In the corporate sector, this is considered to be the most costly option. Expenses from the safe operation, maintenance and development of the system can increase to the extreme.
- IaaS, meaning a kind of Infrastructure Service, where the business uses the IT architecture, the costly servers, storages and theirs network components, including their maintenance and development, as well as backups, logging, and security, as a flexible virtual solution. The applications, databases, operating systems and middleware you run can be operated pecisely according to your needs.
- PaaS – A platform service in which the cloud provider already provides almost all sub-services except applications and in most cases databases. This solution is best for developers.
- SaaS – Software as a service, which is perhaps the best known way to provide and use cloud solutions. There are many sub-models of this, from data service to function service, and even common sets with previous models. The point is that the user can utilize through a browser a full range of software services. In addition to its myriad infrastructural and business benefits, there is perhaps only one real downside, it’s when you have no internet.
And how the virtual service methods are not over here, we also show a short list of solutions we know and use, that we certainly don’t want to analyze in this blog:
- Analytics as a Service
- Authentication as a Service
- Backup as a Service
- Business as a Service
- Communications as a Service
- Computing as a Service
- Content as a Service
- Desktop as a Service
- Energy Storage as a Service
- Games as a Service
- Hardware as a Service
- IT as a Service
- Knowledge as a Service
- Logging as a Service
- Mashups as a Service
- Mobile Backend as a Service
- MongoDB as a Service
- Monitoring as a Service
- Network as a Service
- Oracle as a Service
- Payments as a Service
- Quality as a Service
- Query as a Service
- Recovery as a Service
- Replication as a Service
- Robot as a Service
- Routing as a Service
- Search as a Service
- Security as a Service
- Storage as a Service
- Utilities as a Service
- Virtualization as a Service
- WAN Optimization as as Service
What utilizations are available in the cloud?
Well, depending on what has been written above, it is difficult to say that virtual services or local solutions are ideal for a company. In all cases, the company’s capabilities, needs, available technologies and all influencing factors that affect the operation, use or even regulate data management must be examined.
The most important thing about cloud infrastructure is what it can actually be used for. The majority of enterprises use the “IT” to serve office software and business management systems. This raises the question of what office applications are worth using and what services are not. The answer is not clear here either, because although many companies use business solutions in a similar way, there are not exactly the same two businesses, just as no two have exactly the same needs. This raises another questions of how and why cloud possibilities are used.
In most cases, cost optimization is the reason for cloud usage. In many other cases, it is based on analyzing the totality of the data, embedding business intelligence, or flexible scalability. The solution of Microsoft, the market leader in office softwares, Azure is able to provide an effective response to virtually all needs. This makes all your office applications available in virtual form, from Office software to enterprise management solutions. And business intelligence software provides analytics and statements that would be difficult to extract from locally stored data in a matter of seconds. In addition, a number of commercially and operationally advantageous services can be paired with applications and databases that are not available outside the cloud.
How does Azure work? Watch a short video from Microsoft!
Obviously, Azure as a cloud computing is not much different from other vendors’ cloud, so not only Microsoft software can run on the system, and not just SaaS. Of course, there may be differences, custom or special services between the solutions of different cloud providers, but there are no significant differences in the design and operation of the IT architecture.
On the other hand, the cloud systems differ uniformly from the local architectures, so the applications and databases to be run must be prepared for the possibilities and requirements of the environment. The purpose of the migration may be to use existing applications, but in most cases it may involve the introduction of new business or operational services and processes due to the possibilities provided by the cloud system.
How do you design business and technology strategies for Azure? Watch a short video from Microsoft!
Migration in each case requires significant planning, which is compiled by different working groups. In this preparation process, the goal is not only to get the most out of the functionality, but to develop an entirely new strategy to optimize licensing costs. No less a key issue is the definition of the expected business results, for example the mapping and transformation of business-critical processes to the technological possibilities and advantages provided by the cloud environment.
What provides access control for Azure resources? Watch a short video from Microsoft!
One of the indisputable reasons for the introduction of cloud infrastructure is optimization, but security is not secondary to many aspects. Experience shows that the vulnerabilities of cloud and on-premises systems are not much different, with the users themselves being the main threat. What is in favor of cloud systems, however, is security planning for migration. This is because cloud migration is high risk and expense, so it is necessary to perfect each of its pivotal points. Flawless implementation requires flawless design, so security considerations may be more prominent than in the case of an “aging” local architecture today.
What are the benefits of cloud infrastructure?
Full or partial cloud migration of infrastructure is a costly process, so it would be difficult to say that it will immediately “generate money” as opposed to a local solution. Much of the cost is mostly in preparation for the move, which is not a few days process. It requires a lot of working hours in all cases and also greatly affects business users. Of course, these costs can be kept within reasonable limits, but the cost optimization of the infrastructure does not lie in the implementation of the migration, but in its planning and subsequent operation.
Financial benefits of cost optimization
- License consolidation can reduce access costs and, in some cases, replace or reorganize certain licenses with others available in more favorable contsruct. In our experience, an architecture with a software portfolio of € 50k can be reduced to as much as € 35k in the optimal case.
- You only have to pay for the accesses that are currently needed and used, which can be flexibly changed in the monthly fee constructions.
- Resources that serve computing power can be turned off after business hours, or even for an entire weekend, so they are not a cost.
- Operation requires less human resources, and in the case of optimal deployment, the entire system can be managed without time and geographical constraints. Based on domestic payments, they can mean cost reductions of up to EUR 50-60k per year.
- The power consumption of the sites is not increased by the servers, data storage systems and their redundant units, or the server room devices that ensure continuous operation. These can mean spending cuts of up to € 5-10k a year.
Of course, optimization of costs is not the one and only advantage you can take while you migrate to cloud. There can also be several aspects to a cloud or hybrid solution that indirectly lead to a business advantage. The reorganization or introduction of technological innovations, various processes, controls, analyzes and reporting provides an additional opportunity for successful business and development.
Benefits provided by cloud technology
- Flexible scalability increases not only financial but also organizational and operational flexibility, which can lift up a company’s competitiveness on the certain market.
- Cloud systems provide higher availability and higher performance, as well as they keep the procedure of debugging fast and make recovery easy in the event of any unplanned downtime.
- Deploying intelligence systems, the cloud architecture allows for deeper analysis, allowing more data to be used to make decisions in a specific area.
- You can install new applications and services much faster in the cloud for any group, and on the other hand it provides more complex automation capabilities and new functionality compared to on-premises operations.
- Various competitive market statistics promise more reliable and secure technology in the cloud system of the largest service providers than the available local solutions.
Of course, the individual advantages could still be listed, as the strategies and aspects of the companies may be different, but there may be some disadvantages of cloud solutions compared to local systems. Since the cloud system also means vulnerability, we cannot be sure that everything that is not up to us will work properly. However, the Murphy’s Law, which has been misunderstood by many, must also be used as a basis for moving to cloud to have the least impact on the business. You have to be virtually as alert as you are while driving.
and what to prepare for...
- System downtime, which may be due to service outages but for reasons beyond the control of the business. What can be done about it? Set up multi-regional access zones, set up a dedicated connection (Azure ExpressRoute), choose the highest SLA.
- Issue of security that is based on nothing but real events that have taken place. What can be done about it? Make advanced risk management plan and access management, use encryption at all levels, multifactor authentication, secure platform selection (Azue Blob Storage)
- Portability barriers that can occur if a business wants to move to another provider, but cross-platform migration makes this difficult due to technological differences. What can be done about it? Application of the most common methods in the implementation, taking into account the portability, cloud-optimized solutions, Kubernetes containerization
- High implementation costs, which can be relatively significant, especially for smaller, short-term solutions. What can be done about it? Automatic scaling, options for up and down scaling, service usage monitoring
- Loss of Internet access. What can be done about it? More Internet access service as a redundancy solution for on-premises and critical mobile access
However, the issues listed can occur in much smaller numbers if operators are prepared for it and have an effective, quick recovery plan to fix it. By the way, our experience shows that, in fact, the 999 SLAs are also quite satisfactory (99.9% availability = about 8 hours downtime in one year), and this is considered an acceptable risk even by really big companies.
In fact, and perhaps this is the most acceptable alternative, you don’t necessarily have to move everything to the cloud. Real reasons for this may include certain privacy restrictions or compliance criteria. Hybrid solutions provide a safe alternative to exactly the critical points that companies fear most in management. The hybrid cloud and on-premises infrastructure can be kept in optimal harmony, and in many cases it can be more preferable than to use only cloud or only on-prem architecture. By focusing on the benefits of technology and ensuring business continuity, it is possible to build good operating models in almost any industry. Not to mention using a private cloud, which can also mean higher security for critical data or applications.